Preload allows you to specify resources (such as fonts, images, JavaScript, and CSS) that are needed right away or very soon during a page load. A link rel tag is added toward the top of the <head> </head> section on every page of your site.
<link rel='preload' href='font.woff2' as='font' type='font/woff2' crossorigin>
This helps fix the following two types of warnings:
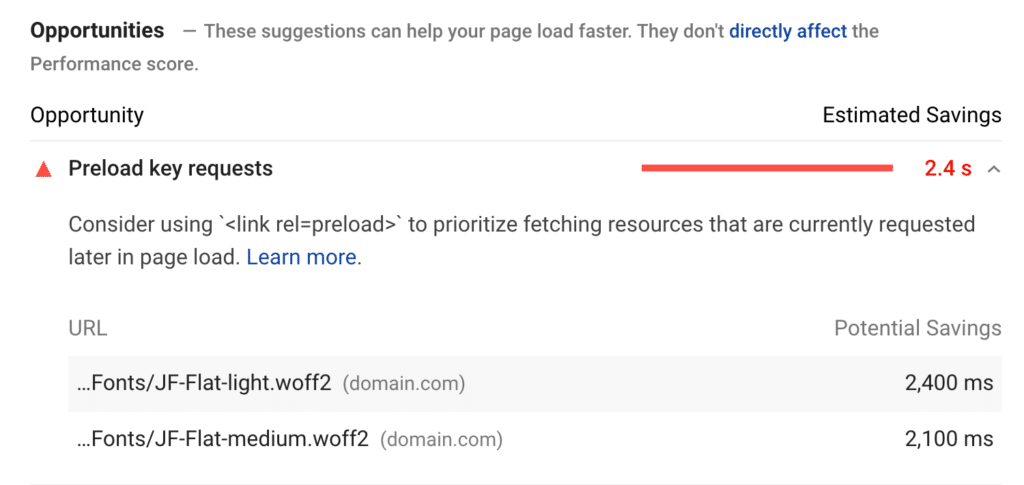
1. Preload key requests
Preload key requests is a common warning with web fonts. Font Awesome is a very common one you might see show up.
2. Render-blocking resources
By preloading, you can also fix the render-blocking resource warning as assets are loaded in a non-blocking manner.

Beyond fixing the warnings, preloading resources (such as images above the fold) can help greatly improve Largest Contentful Paint (LCP).
Dive into Perfmatters preload features below.
Preloadable resources
There are many different resources that can be preloaded. Below are the formats that are supported in the Perfmatters plugin:
Common resources
font: Font file.script: JavaScript file.style: CSS stylesheet.image: Image file (.jpg,.png,.webp,.avif).
Additional resources
audio: Audio filedocument: An HTML document intended to be embedded by a<frame>or<iframe>.embed: A resource to be embedded inside an<embed>element.fetch: Resource to be accessed by a fetch or XHR request, such as an ArrayBuffer or JSON file.object: A resource to be embedded inside an<object>element.track: WebVTT file.worker: A JavaScript web worker or shared worker.video: Video file. This isn’t supported in Chrome. However, browsers automatically optimize MP4/WebM files. So a preload on videos isn’t necessary.
Implement preload in WordPress
Preload is supported by all modern browsers, with the exception of Internet Explorer (Microsoft Edge supports it) and Opera Mini. Note: Preload was added to Firefox in version 85.
To preload a resource, follow the steps below.
Step 1
Click into the Perfmatters plugin settings.
Step 2
Click on the “Preloading” menu.
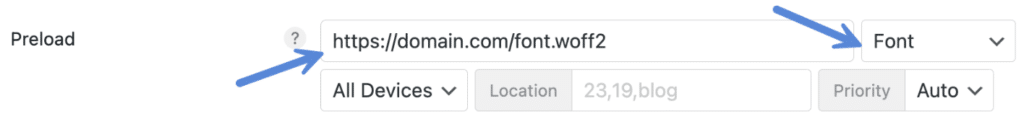
Step 3
Under “Preload” enter in the location of your resource. This should be the full URL. Example: https://domain.com/font.woff2.
Then select the type of resource it is (font, image, script (JS), style (CSS), etc.).
Preloading by device
By default, it will preload the resource on all devices. However, you can choose desktop or mobile if needed. To use mobile preloads, you’ll need to ensure you have separate mobile caching enabled:
- Most hosting providers with server-level cache already have separate caching buckets for devices in place, which means you don’t need to do anything.
- If you’re using Cloudflare APO, you can enable cache by device type.
- If you’re using edge cache from a hosting provider, they will sometimes have a separate mobile cache option. For example, Kinsta edge cache has this.
- If you’re using a caching plugin like WP Rocket or Cache Enabler, many have a separate mobile cache option.
Preloading location
You can also set a location. Perhaps you need to preload an image just on your homepage, but nowhere else. Remember, preload will forcefully load the resource regardless, so you don’t want to preload something that isn’t needed. Use blog if your homepage is a blog feed. Otherwise, add the post ID. You can add multiple locations, comma-separated.
You can find the post ID by editing a post or page in the WordPress Block Editor. The post ID will show in your browser’s address bar.
Note: If you have two different physical pages in WordPress that switch based on desktop or mobile, you’ll most likely need to use the post ID of your desktop homepage but then select “mobile” for the device.
Preloading priority
You can choose a priority (auto, high, or low) when preloading a resource. Typically “auto” is fine. However, if you are preloading an LCP image, this is one instance where you will want to use the “high” value.
Step 4
Scroll down and click “Save Changes.”
Note: If you are having problems seeing your changes show up in a performance testing tool, make sure to clear your URL or site’s cache before testing it.
Dynamic preloads
Browsers require the exact URL for preloads to work. So if you have resources (CSS, JavaScript) with query strings on them, it can be helpful to preload them dynamically using their handle. This means the query string on the end will automatically get updated as the version changes, or as you update WordPress core, etc. And this saves you from having to update them manually.
For example, take the WordPress Block Library stylesheet. It gets the current version of WordPress core automatically appended to it.
/wp-includes/css/dist/block-library/style.min.css?ver=5.8.1Each properly enqueued WordPress script or stylesheet has a handle attached to it, which you can view in the Script Manager. For the WordPress Block Library stylesheet, you can see the handle is wp-block-library. You can then add the handle in the preload section of Perfmatters instead of the full URL of the resource.
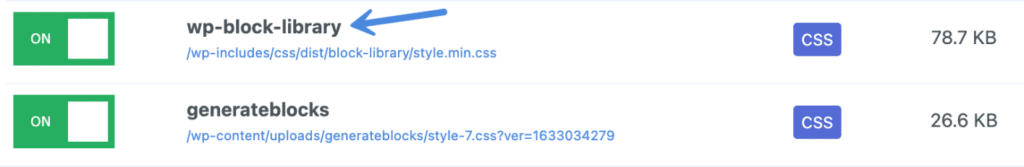
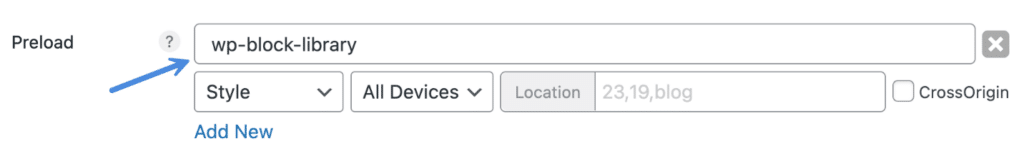
So for example, if you wanted to preload the WordPress Block Library stylesheet, you would add the following handle: wp-block-library. The preload will then automatically get updated with the current query string version.
Preload critical images
Preloading leading images (those above the fold) can help decrease Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) times in Core Web Vitals. These are typically images like a logo, a featured image on a blog post, a hero image on a landing page, etc. By preloading them, you’re moving them to the top of the waterfall and essentially telling the browser that these have priority and should be loaded right away.
The Preload Critical Images feature in Perfmatters will automatically preload the number of leading images that you choose (0-5).
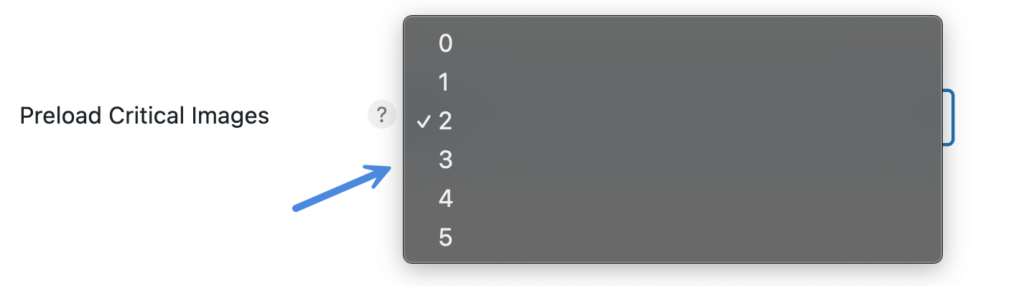
It’s important to understand that Chrome has a limit of two image preloads that will appear at the very top of the waterfall. Anything after two will still appear higher in the waterfall but will not be as high priority, and this is entirely up to Chrome. We usually recommend using 2-3. This will typically preload your logo and say a featured image in a blog post.
If you have a manual image preload on a page, this will take precedence over one of the automatic preloads.
The preloading critical images feature will also automatically exclude those images from lazy loading.
How to filter preloads
You can use the perfmatters_preloads filter to manipulate your manual preloads. For example, you could remove a specific preload from printing.
add_filter('perfmatters_preloads', function($preloads) {
foreach($preloads as $key => $preload) {
if($preload['url'] == 'https://example.com/style.css') {
//custom code
unset($preloads[$key]);
}
}
return $preloads;
});
If you are using our Preload Critical Images feature, you can use the perfmatters_critical_image_exclusions filter to exclude certain images from being preloaded.
add_filter('perfmatters_critical_image_exclusions', function($exclusions) {
$exclusions[] = 'example.png';
return $exclusions;
});
See our other preload filters to fine-tune things even further.
Things to keep in mind when preloading
How to find Local Google Fonts to preload
If you’re using Perfmatters Local Google Fonts along with Display Swap, preloading the fonts will help prevent any Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
Google has many variations for different languages, but you only need to preload the fonts the browser is loading. To find these, we recommend looking in the waterfall using Chrome DevTools or GTmetrix. In this example, you see we have three local Google Fonts loading.
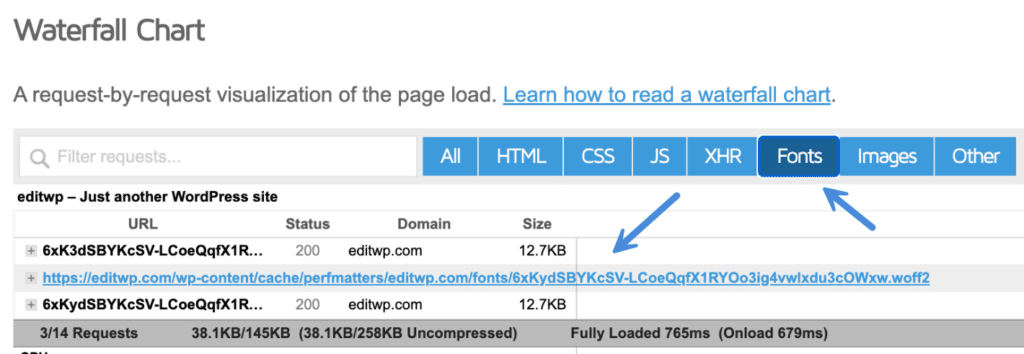
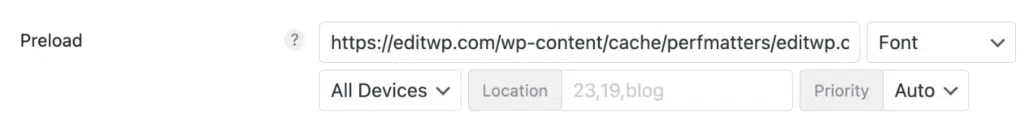
You will want to copy the full URL of each font and input it into the preload section in Perfmatters. Make sure to select “Font” as the resource type.
Additional tips
- Don’t preload every script or it will actually cause performance issues, such as increasing total blocking time (TBT). Preloading should only be used for resources that are needed immediately, so they are loaded in a non-blocking manner. Typically this used for web fonts, images, CSS, and JS.
- If you’re using cache-busting techniques (such as query strings
domain.com/style.css?ver=1.0), don’t forget that browsers see exact URLs. So you will need to use the query string URL or you can preload dynamically with a handle. - If you have a CDN rewriting your asset’s URLs, ensure that all the resources you want to preload are first getting rewritten properly. If the URLs don’t match up, you could end up loading a resource twice.
- If you preload a stylesheet (CSS) or script (JS) and you’re using a plugin to combine your CSS/JSS (Autoptimize, WP Rocket, etc.), make sure to exclude the resource your preloading from the concatenation process. Otherwise, it could get wrapped up twice and end up putting more code on your site.
- If you’re using Elementor, there are a few tricks you can use to load your hero images as normal images so that optimization plugins can handle them better.